Retinal Detachment
What is Retinal Detachment?
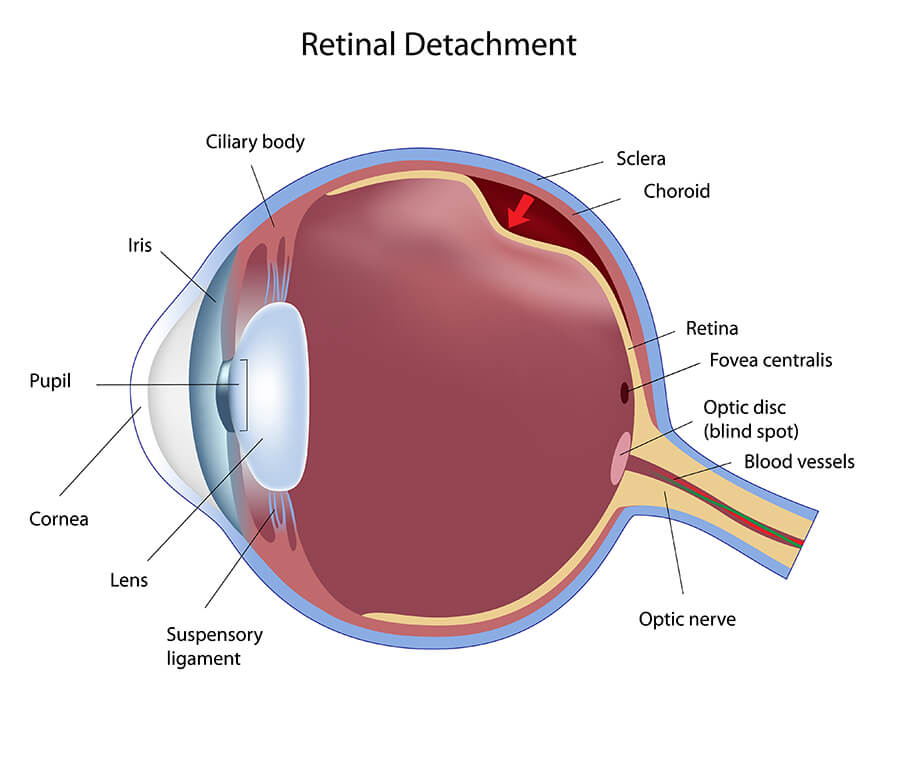
Retinal detachment is a serious eye condition that occurs when the retina becomes separated from the wall of the eye and its supportive underlying tissue. The retina cannot function when these two layers are detached, and without prompt treatment, permanent vision loss may occur. Retinal detachment can occur from injury to the eye or face, or from very high levels of nearsightedness.
Patients with retinal detachment may experience a blind spot, blurred vision or shadows forming in their peripheral vision. Other symptoms may include an increase in flashes and floaters. It is important to see your doctor at the first sign of symptoms in order to minimize the damage caused by this condition.

To prevent permanent vision loss, the retina must be quickly reattached. Treatment for retinal detachment can be done through surgery or laser photocoagulation. Photocoagulation seals off leaking blood vessels and destroys new blood vessel growth, allowing the retina to reattach. Pneumatic retinopexy, a procedure that creates a gas bubble within the vitreous gel and then expands to place pressure against the retina, can also help with reattachment.
These procedures can preserve vision and may also allow lost vision to return in some patients. The sooner the retina is attached, the more effective treatment tends to be. If you are experiencing signs of retinal detachment, please call us immediately.
Flashes And Floaters
Although most flashes and floaters occur in people with healthy or merely nearsighted eyes, they can be symptoms of serious problems including injury and retinal and posterior vitreous detachments. Flashes in vision are caused by pressure on the retina, the bundle of nerves in the back of the eye where images are detected and transmitted to the brain. Patients complain of flashing lights or lightning streaks.
Floaters are often seen when fibers move within the vitreous humor, the gelatinous substance made of water and protein fibers that fills the eye. Patients complain of small specks or dots that can be seen against clear backgrounds. Serious vision loss can occur if the retina or vitreous detach from the eye wall. Patients experiencing flashes and floaters should contact their doctor immediately so an examination can be performed.